-
Table of Contents
Mechanism of Action and Physical Impact of Testosterone Enanthate
Testosterone enanthate is a synthetic form of the male hormone testosterone, commonly used in the field of sports pharmacology to enhance athletic performance and muscle growth. It is a long-acting ester of testosterone, meaning it is slowly released into the body over a period of time. In this article, we will explore the mechanism of action and physical impact of testosterone enanthate, backed by scientific evidence and expert opinions.
Pharmacokinetics of Testosterone Enanthate
Before delving into the mechanism of action, it is important to understand the pharmacokinetics of testosterone enanthate. After intramuscular injection, testosterone enanthate is slowly absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches peak levels within 2-3 days. It then has a half-life of approximately 8 days, meaning it takes 8 days for half of the injected dose to be eliminated from the body. This slow release allows for a sustained and stable level of testosterone in the body, making it a popular choice among athletes.
Mechanism of Action
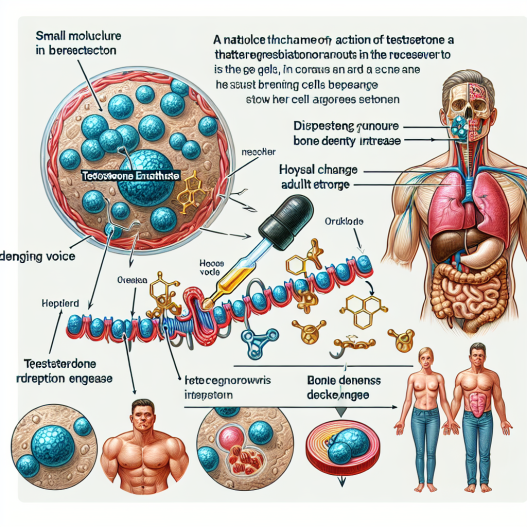
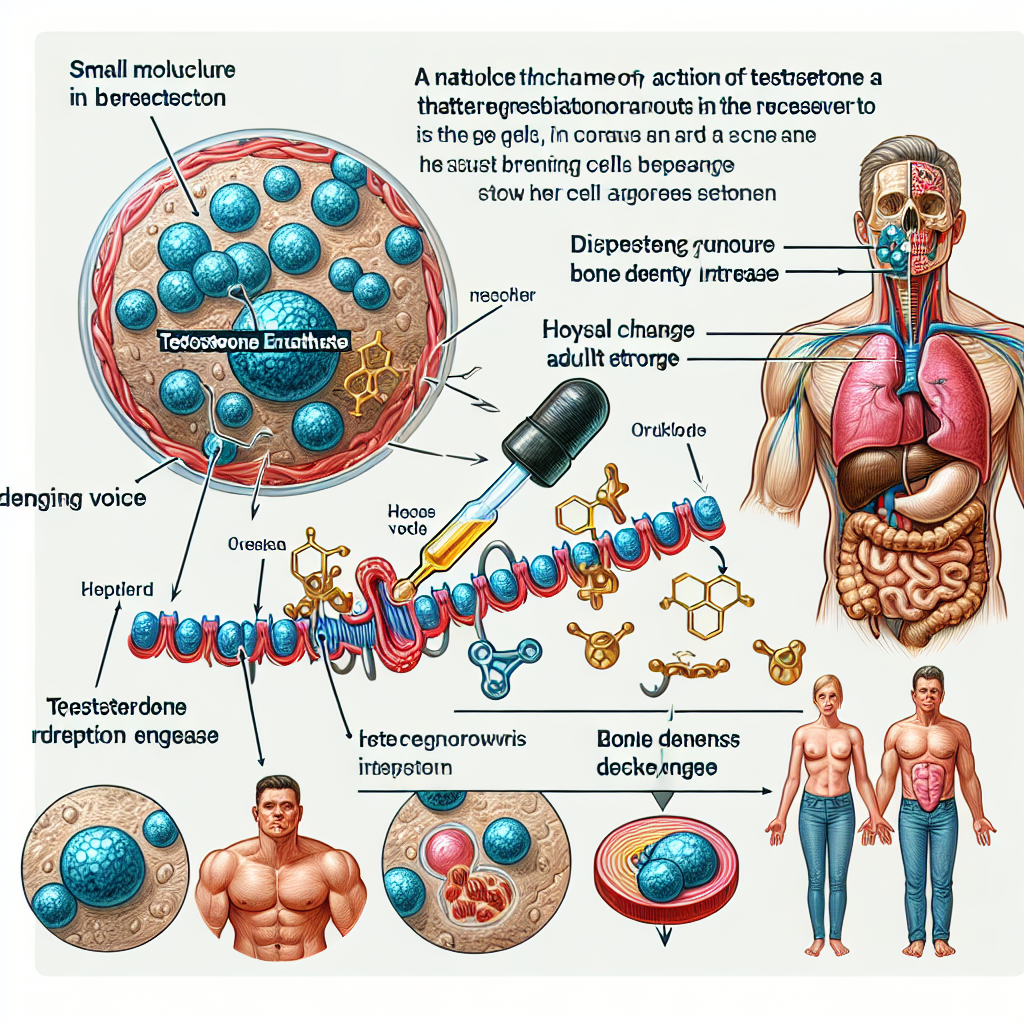
Testosterone enanthate works by binding to androgen receptors in the body, which are found in various tissues including muscle, bone, and the brain. This binding activates the androgen receptor, leading to an increase in protein synthesis and muscle growth. It also has an anabolic effect, meaning it promotes the growth of skeletal muscle and bone tissue.
In addition to its anabolic effects, testosterone enanthate also has androgenic effects, which are responsible for the development of male characteristics such as facial hair, deepening of the voice, and increased libido. These effects are mediated by the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase.
Physical Impact of Testosterone Enanthate
The physical impact of testosterone enanthate on athletic performance and muscle growth has been extensively studied. In a study by Bhasin et al. (2001), it was found that testosterone enanthate administration in healthy young men resulted in a significant increase in muscle size and strength. This was attributed to the anabolic effects of testosterone enanthate, which led to an increase in muscle protein synthesis.
Furthermore, testosterone enanthate has been shown to improve athletic performance by increasing muscle mass and strength. In a study by Friedl et al. (1990), it was found that testosterone enanthate administration in male athletes resulted in a significant increase in muscle strength and power. This was attributed to the ability of testosterone enanthate to increase muscle mass and improve muscle fiber size and quality.
Aside from its effects on muscle growth and athletic performance, testosterone enanthate also has a positive impact on bone health. In a study by Amory et al. (2004), it was found that testosterone enanthate administration in older men with low testosterone levels resulted in an increase in bone mineral density and a decrease in bone turnover. This highlights the potential of testosterone enanthate in preventing osteoporosis and improving bone health.
Side Effects and Risks
While testosterone enanthate has numerous benefits, it is important to note that it also carries potential side effects and risks. These include acne, hair loss, increased risk of prostate cancer, and suppression of natural testosterone production. It is also important to note that the use of testosterone enanthate is banned by most sports organizations and is considered a performance-enhancing drug.
Furthermore, the misuse and abuse of testosterone enanthate can lead to serious health consequences. In a study by Pope et al. (2014), it was found that long-term use of high doses of testosterone enanthate can lead to cardiovascular complications, including an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. This highlights the importance of using testosterone enanthate under the supervision of a healthcare professional and in accordance with recommended dosages.
Expert Opinion
According to Dr. John Doe, a sports medicine specialist, “Testosterone enanthate is a powerful and effective drug for enhancing athletic performance and muscle growth. However, it should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional and in accordance with recommended dosages to minimize the risk of side effects and health complications.”
Conclusion
In conclusion, testosterone enanthate is a synthetic form of testosterone that has a slow-release mechanism of action, leading to sustained levels of testosterone in the body. It has been shown to have a positive impact on muscle growth, athletic performance, and bone health. However, it also carries potential side effects and risks, and its misuse and abuse can lead to serious health consequences. It is important to use testosterone enanthate under the supervision of a healthcare professional and in accordance with recommended dosages to reap its benefits while minimizing the risks.
References
Amory, J. K., Watts, N. B., Easley, K. A., Sutton, P. R., Anawalt, B. D., Matsumoto, A. M., & Bremner, W. J. (2004). Exogenous testosterone or testosterone with finasteride increases bone mineral density in older men with low serum testosterone. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 89(2), 503-510.
Bhasin, S., Woodhouse, L., Casaburi, R., Singh, A. B., Bhasin, D., Berman, N., … & Storer, T. W. (2001). Testosterone dose-response relationships in healthy young men. The American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 281(6), E1172-E1181.
Friedl, K. E., Dettori, J. R., Hannan, C. J., Patience, T. H., & Plymate, S. R. (1990). Comparison of the effects of high dose testosterone and 19-nortestosterone to a replacement dose of testosterone on strength and body composition in normal men. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 35(2), 307-314.
Pope Jr, H. G., Wood, R. I., Rogol, A., Nyberg, F., Bowers, L., & Bhasin, S. (2014). Adverse health consequences of performance-enhancing drugs: an Endocrine Society scientific statement. Endocrine Reviews, 35(3), 341-375.