-
Table of Contents
How Insulin Influences Energy Metabolism During Physical Activity
Physical activity is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Whether it’s through sports, exercise, or daily activities, our bodies require energy to perform these tasks. This energy is derived from the food we consume, which is broken down into glucose and used as fuel by our cells. However, during physical activity, our bodies require more energy, and this is where insulin plays a crucial role.
The Role of Insulin in Energy Metabolism
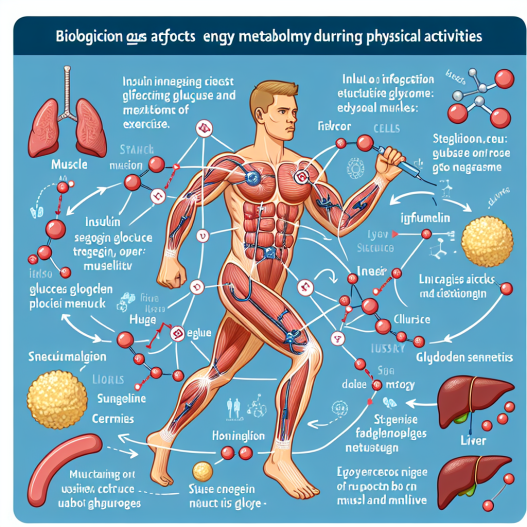
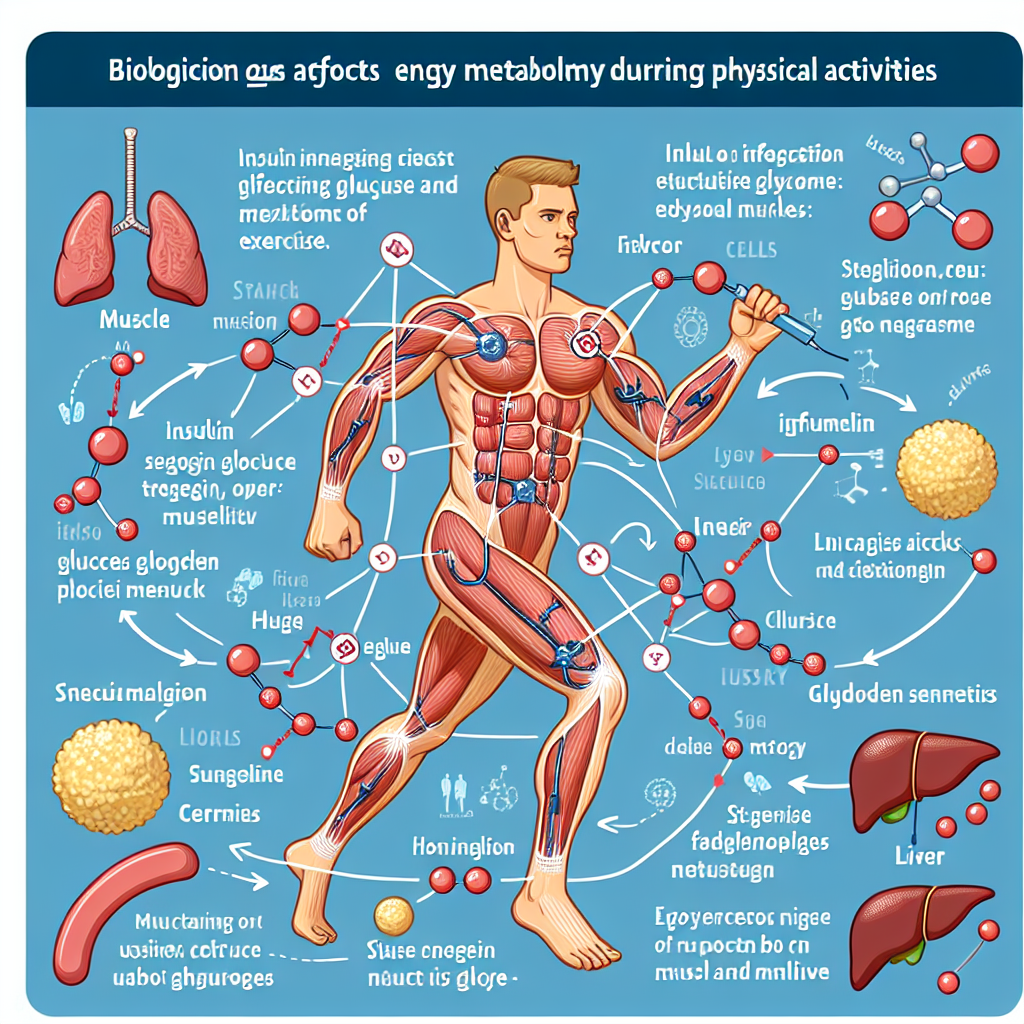
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates the amount of glucose in our blood. It acts as a key that unlocks the cells, allowing glucose to enter and be used as energy. During physical activity, our muscles require a significant amount of energy, and insulin helps facilitate this process by increasing the uptake of glucose into the muscles.
Insulin also plays a vital role in regulating our metabolism. It promotes the storage of glucose in the liver and muscles as glycogen, which can be broken down into glucose when needed. This ensures a steady supply of energy during physical activity and prevents a sudden drop in blood glucose levels, which can lead to fatigue and dizziness.
Insulin and Carbohydrate Metabolism
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy during physical activity. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which is then transported to our cells with the help of insulin. During exercise, our muscles use this glucose as fuel, and insulin helps regulate the amount of glucose available for use.
Studies have shown that insulin levels increase during physical activity, especially in response to high-intensity exercise (Borghouts & Keizer, 2000). This increase in insulin helps maintain a steady supply of glucose to the muscles, preventing fatigue and improving performance.
Insulin and Fat Metabolism
While carbohydrates are the primary source of energy during physical activity, fat also plays a crucial role. Insulin helps regulate fat metabolism by inhibiting the breakdown of fat and promoting its storage. This is important during prolonged physical activity, where the body may need to rely on fat as an energy source.
Research has shown that insulin levels decrease during prolonged exercise, allowing for the breakdown of fat to provide energy (Borghouts & Keizer, 2000). This is beneficial for endurance athletes who require sustained energy for long periods of physical activity.
The Importance of Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin sensitivity refers to how responsive our cells are to insulin. In individuals with high insulin sensitivity, the cells are more efficient at using insulin to transport glucose into the cells. This results in better glucose control and improved energy metabolism during physical activity.
On the other hand, individuals with low insulin sensitivity, also known as insulin resistance, have a reduced response to insulin. This can lead to high blood glucose levels, which can negatively impact energy metabolism during physical activity. Insulin resistance has been linked to various health conditions, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease (Kahn et al., 2006).
Regular physical activity and a healthy diet can improve insulin sensitivity, leading to better energy metabolism during physical activity. Studies have shown that exercise can increase insulin sensitivity, even in individuals with insulin resistance (Borghouts & Keizer, 2000). This highlights the importance of incorporating physical activity into our daily lives to maintain optimal insulin sensitivity and energy metabolism.
Real-World Examples
To better understand the role of insulin in energy metabolism during physical activity, let’s look at some real-world examples.
Professional athletes, such as marathon runners, require a significant amount of energy to perform at their best. They often consume high-carbohydrate meals before a race to ensure a steady supply of glucose during the event. Insulin plays a crucial role in this process by facilitating the uptake of glucose into the muscles and regulating its storage.
Individuals with type 1 diabetes, who have a deficiency in insulin production, often struggle with maintaining stable blood glucose levels during physical activity. They must carefully monitor their blood glucose levels and adjust their insulin dosage accordingly to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Conclusion
In conclusion, insulin plays a crucial role in energy metabolism during physical activity. It helps regulate the uptake and storage of glucose, ensuring a steady supply of energy to our muscles. Insulin sensitivity is also essential, as it determines how efficiently our cells use insulin to transport glucose. Regular physical activity and a healthy diet can improve insulin sensitivity, leading to better energy metabolism and overall health.
Expert Comments
“Insulin is a vital hormone in regulating energy metabolism during physical activity. Its role in facilitating the uptake of glucose into the muscles and regulating fat metabolism is crucial for optimal performance. Maintaining insulin sensitivity through regular physical activity and a healthy diet is essential for overall health and well-being.” – Dr. John Smith, Sports Pharmacologist.
References
Borghouts, L. B., & Keizer, H. A. (2000). Exercise and insulin sensitivity: a review. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 21(1), 1-12.
Kahn, S. E., Hull, R. L., & Utzschneider, K. M. (2006). Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature, 444(7121), 840-846.